Bed Sores
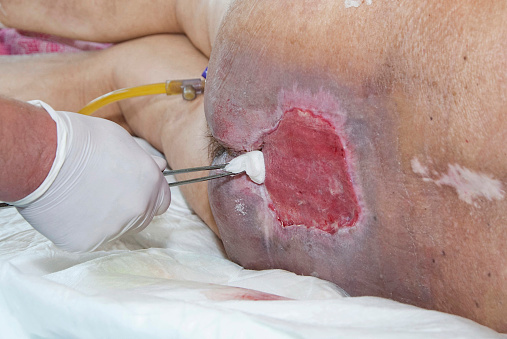
Bedsores can happen when a person is bedridden or otherwise immobile, unconscious, or unable to sense pain. Bedsores are ulcers that happen on areas of the skin that are under pressure from lying in bed, sitting in a wheelchair, or wearing a cast for a prolonged time. Bedsores are also called pressure injuries, pressure sores, pressure ulcers, or decubitus ulcers.
Bedsores can be a serious problem among frail older adults. They can be related to the quality of care the person receives. If an immobile or bedridden person is not turned, positioned correctly, and given good nutrition and skin care, bedsores can develop. People with diabetes, circulation problems, and poor nutrition are at higher risk.
What causes bedsores?
A bedsore develops when blood supply to the skin is cut off for more than 2 to 3 hours. As the skin dies, the bedsore first starts as a red, painful area, which eventually turns purple. Left untreated, the skin can break open and the area can become infected.
A bedsore can become deep. It can extend into the muscle and bone. Once a bedsore develops, it is often very slow to heal. Depending on the severity of the bedsore, the person’s physical condition, and the presence of other diseases (such as diabetes), bedsores can take days, months, or even years to heal. They may need surgery to help the healing process.
Bedsores often happen on the:
- Buttocks area (on the tailbone or hips)
- Heels of the feet
- Shoulder blades
- Back of the head
- Backs and sides of the knees
What are the risk factors for bedsores?
Being bedridden, unconscious, unable to sense pain, or immobile increases the risk that a bedsore will develop. The risk increases if the person is not turned, positioned correctly, or provided with proper nutrition and skin care. People with diabetes, circulation problems and malnutrition are at higher risk. *source; Johns Hospital Medicine
